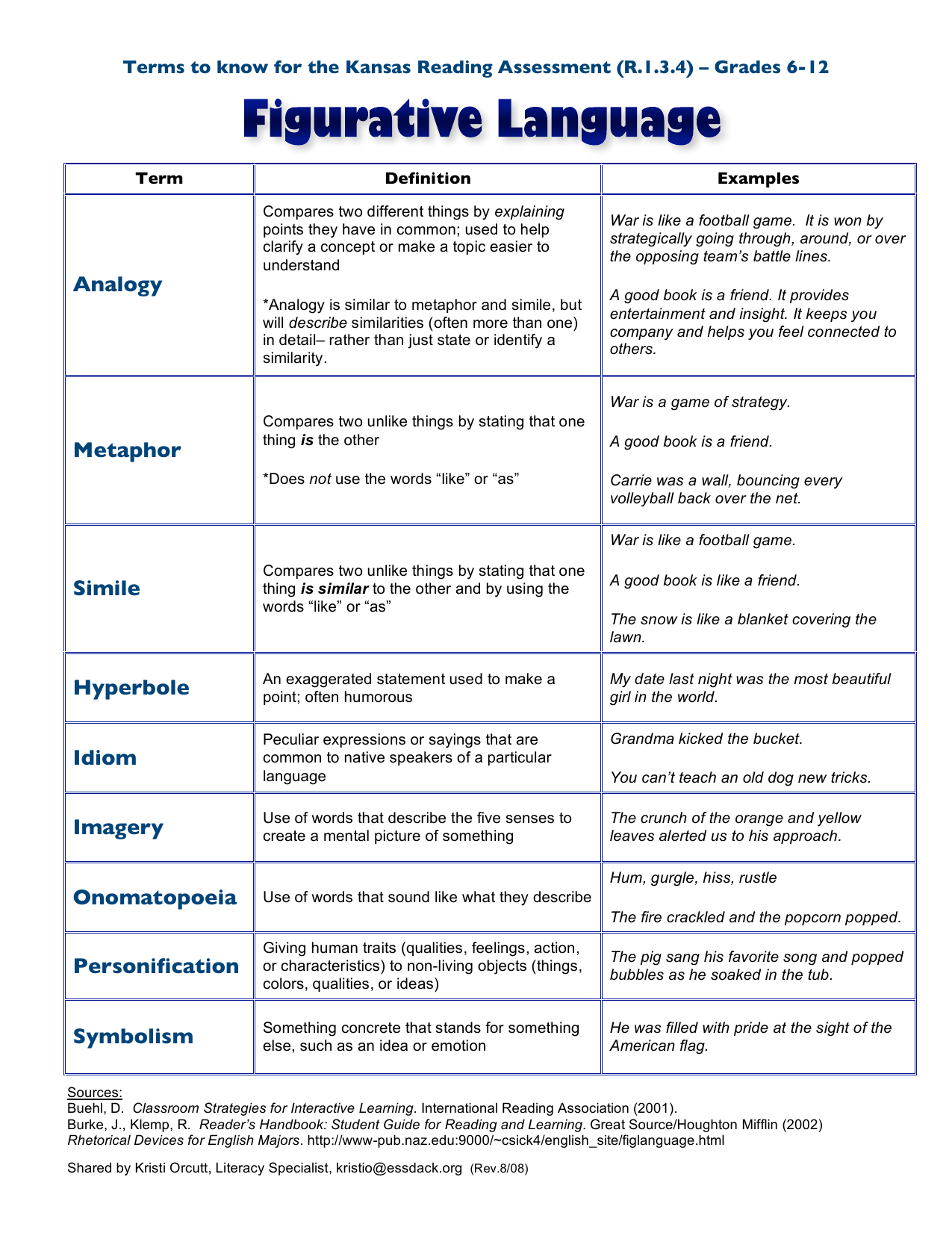
The art of using words to paint vivid pictures in our minds is a powerful tool that has been employed by writers, poets, and storytellers for centuries. Figurative language is a way to add depth, emotion, and complexity to our writing and speech, making it more engaging, expressive, and memorable. In this article, we will explore six types of figurative language that are suitable for all ages, from children to adults.
What is Figurative Language?
Before we dive into the six types of figurative language, let's define what it is. Figurative language is a way of using words to convey meaning beyond their literal interpretation. It involves using language in a non-literal way to create vivid imagery, evoke emotions, and add depth to our writing and speech. Figurative language is used to describe abstract ideas, concepts, and feelings, making it a powerful tool for communication.
1. Simile
A simile is a type of figurative language that compares two unlike things using the words "like" or "as." It is used to create vivid and memorable descriptions by highlighting the similarities between two things. For example:
- "He ran like a cheetah" (comparing a person's running ability to that of a cheetah)
- "She sings as sweetly as a bird" (comparing a person's singing voice to that of a bird)

2. Metaphor
A metaphor is a type of figurative language that compares two unlike things without using "like" or "as." It is used to create a direct comparison between two things, often to describe an abstract idea or concept. For example:
- "He is a lion on the soccer field" (comparing a person's behavior to that of a lion)
- "Life is a journey" (comparing life to a journey)

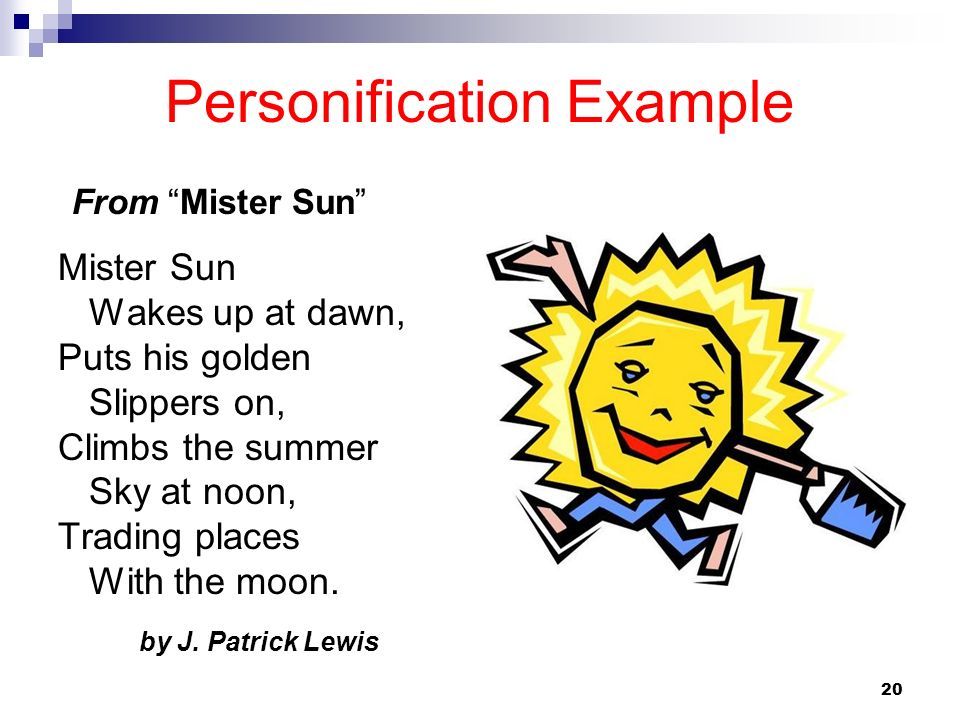
3. Personification
Personification is a type of figurative language that gives human-like qualities to non-human things, such as objects, animals, or ideas. It is used to create vivid and imaginative descriptions by attributing human characteristics to non-human things. For example:
- "The sun smiled down on us" (giving the sun human-like qualities)
- "The wind whispered through the trees" (giving the wind human-like qualities)

4. Hyperbole
A hyperbole is a type of figurative language that involves an exaggeration used for emphasis or effect. It is used to create a strong impression or to highlight a particular point. For example:
- "I'm so hungry I could eat a whole elephant" (exaggerating one's hunger)
- "This backpack weighs a ton" (exaggerating the weight of the backpack)

5. Alliteration
Alliteration is a type of figurative language that involves the repetition of initial consonant sounds in words that are close together. It is used to create a musical or rhythmic effect in language. For example:
- "She sells seashells by the seashore" (repeating the "s" sound)
- "The fluffy feline frolicked in the field" (repeating the "f" sound)

6. Onomatopoeia
Onomatopoeia is a type of figurative language that involves words that imitate the sounds they describe. It is used to create vivid and sensory descriptions by replicating the sounds of the real world. For example:
- "The firework exploded with a loud boom" (imitating the sound of the firework)
- "The raindrops pattered against the window" (imitating the sound of the raindrops)

Conclusion: The Power of Figurative Language
Figurative language is a powerful tool that can add depth, emotion, and complexity to our writing and speech. By using similes, metaphors, personification, hyperbole, alliteration, and onomatopoeia, we can create vivid and memorable descriptions that engage and inspire our audience. Whether we are writing a story, a poem, or a speech, figurative language can help us to convey our ideas and emotions in a way that is both effective and expressive.
Gallery of Figurative Language Examples



FAQs
What is the difference between a simile and a metaphor?
+A simile is a comparison between two unlike things using "like" or "as," while a metaphor is a direct comparison between two unlike things without using "like" or "as."
How can I use alliteration in my writing?
+Alliteration can be used to create a musical or rhythmic effect in language by repeating initial consonant sounds in words that are close together. For example, "She sells seashells by the seashore" repeats the "s" sound.
What is the purpose of onomatopoeia in writing?
+Onomatopoeia is used to create vivid and sensory descriptions by replicating the sounds of the real world. It can help to engage and immerse the reader in the story.